3D Printing Then Vs Now
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has come a long way since its inception. The technology, which allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects by building up layers of material, was first developed in the 1980s. However, it wasn't until the 21st century that 3D printing began to gain widespread attention and adoption.
“Innovation is taking two things that exist and putting them together in a new way.“
When 3D printing first emerged, the technology was primarily used for prototyping in the industrial and manufacturing sectors.
The machines were large, expensive, and required specialized knowledge to operate. Additionally, the materials that could be used for 3D printing were limited, and the resolution and quality of the printed objects were not very high.
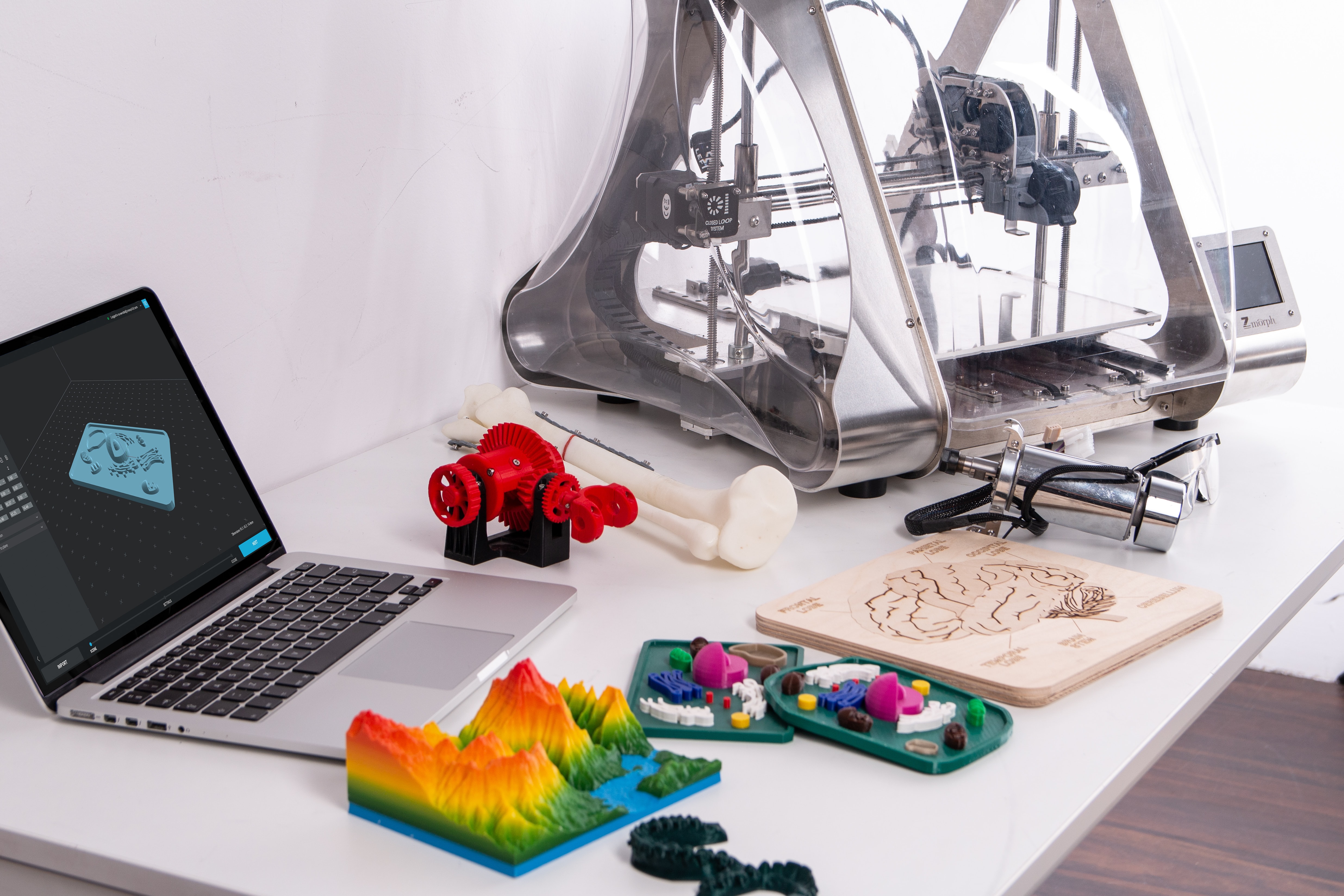

Fast forward to today, and 3D printing has evolved significantly. The machines have become smaller, more affordable, and more user-friendly.
This has led to a proliferation of 3D printing in small businesses, schools, and even homes. Additionally, the materials that can be used for 3D printing have greatly expanded and now include metals, ceramics, and even food.
Furthermore, the technology has become more sophisticated, with the introduction of multi-material and multi-color printing, allowing for more complex and detailed objects to be printed.
Alongside, software and workflow now allow for a wider range of industries to adopt the technology, and the increasing availability of online platforms for buying and selling 3D printable files, it has become more democratized.
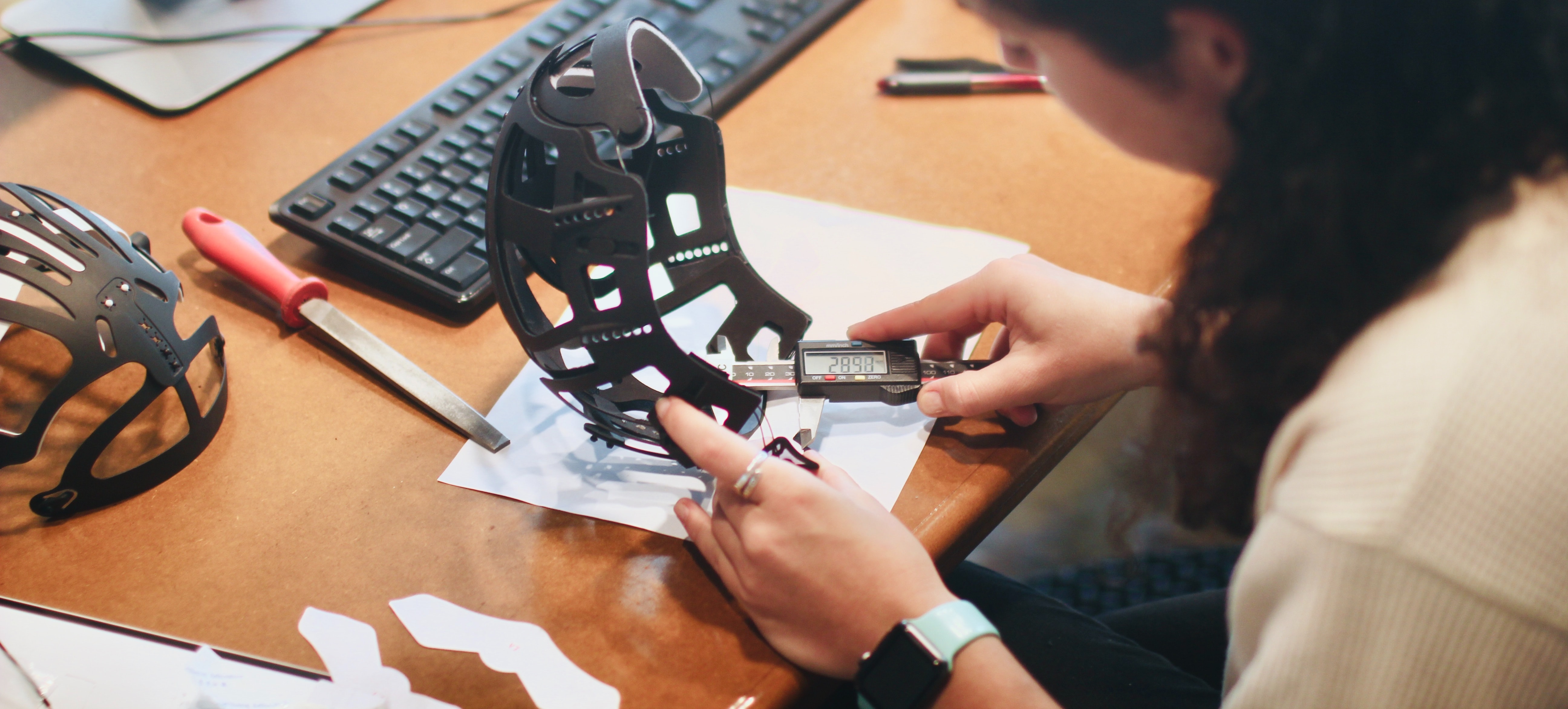

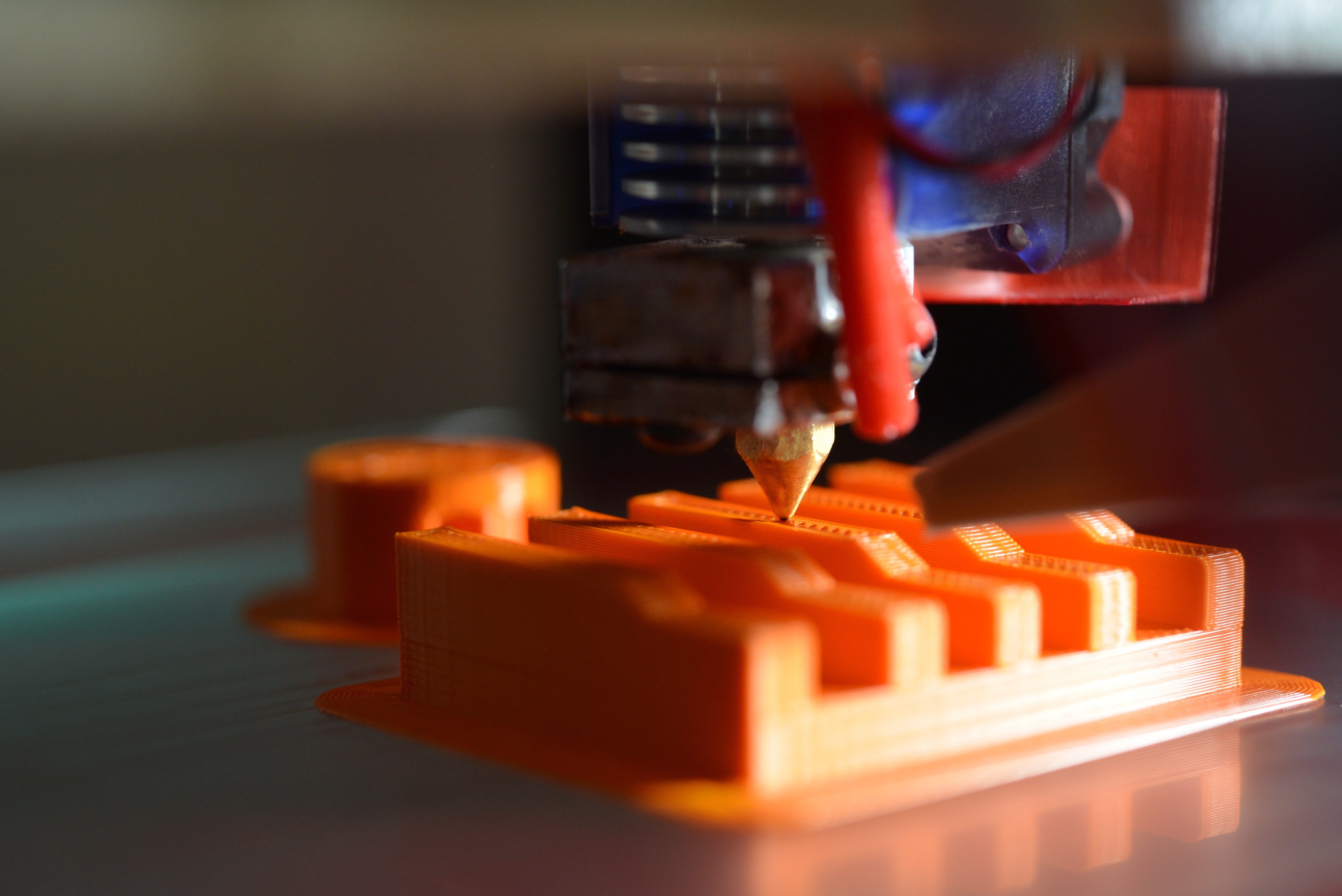
One of the most significant developments in 3D printing has been the advent of FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling) , or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) .
This technology, which uses a filament of material that is melted and extruded through a nozzle to build up layers, is relatively simple and affordable, making it accessible to a wider range of users.
The popularity of FDM 3D printing has also led to a thriving ecosystem of materials, software, and accessories, which makes it easy for users to customize and optimize their machines for specific applications.
Another major development has been the advent of SLA (stereolithography) technology, which allows for high-resolution printing with a wide range of materials.
SLA 3D printing works by curing a liquid resin layer by layer using a UV laser. This process allows for the creation of highly detailed and accurate parts and prototypes.
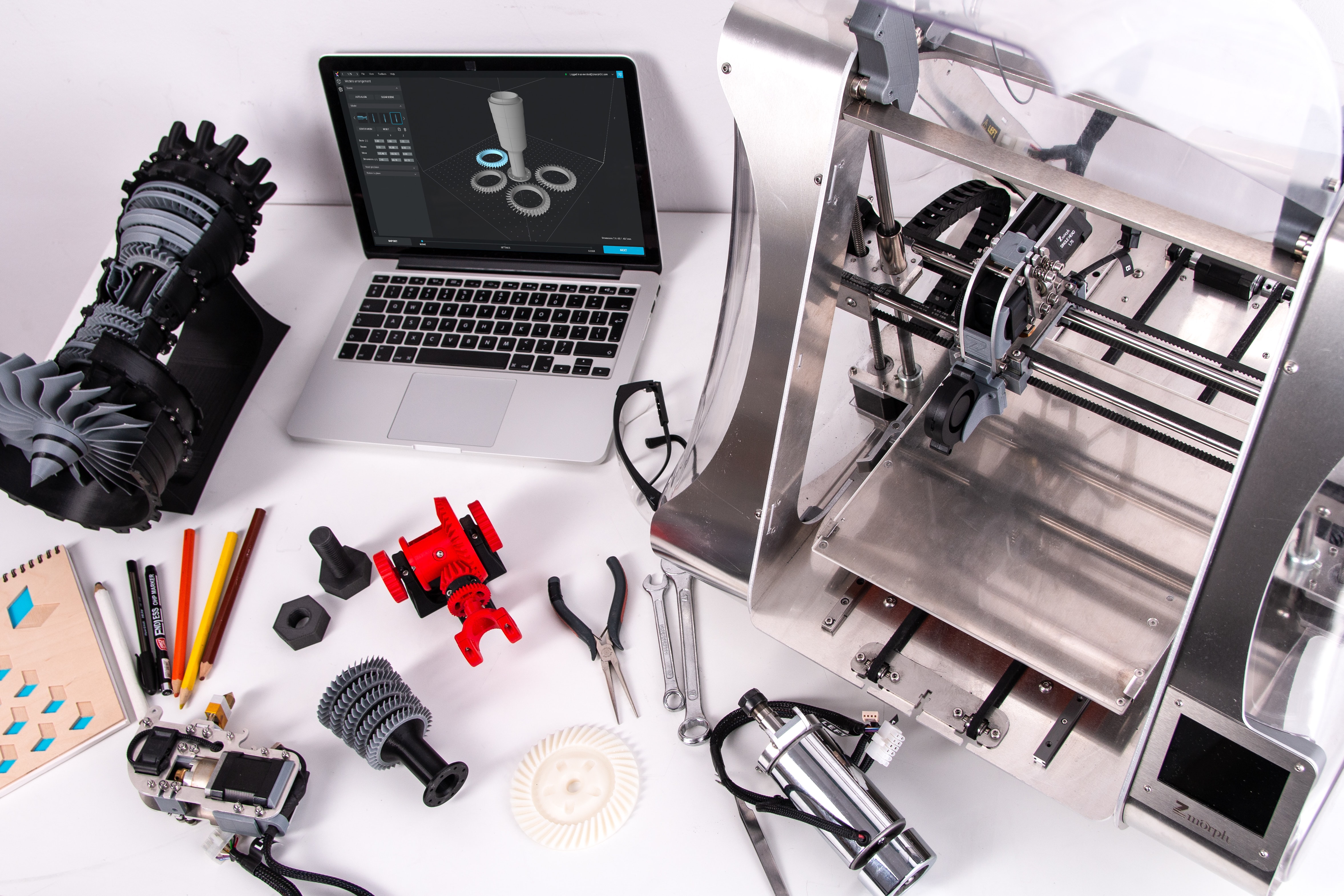

3D printing has also seen applications in various domains like healthcare, automotive, aerospace, fashion and even food industry, as it allows for customization and personalization of products.
In the healthcare industry, 3D printing is used to create prosthetic limbs, dental implants, and even human tissue. In the automotive industry, it is used to create complex and lightweight parts for cars. In aerospace, it is used to create rocket engine parts and satellites.
Additionally, it has been used in fashion to create clothing and jewelry, and in the food industry to create edible sculptures and confections.
However, 3D printing has not yet fully entered into the mainstream.
While the technology has come a long way, there are still challenges to be overcome. The cost of 3D printing, materials and equipment are still an issue for many, as is the lack of standardization and regulations around the technology.
Additionally, the environmental impact of 3D printing is still being studied.
Despite these challenges, it's clear that 3D printing has come a long way since its inception, and it will likely continue to evolve and grow in the coming years.
As the technology becomes more accessible, affordable, and versatile, we can expect to see 3D printing being used in a wider range of applications, from manufacturing to art to food.
Conclusion
3D printing has come a long way since its first introduction and has proven itself to be a powerful and versatile technology.
From its humble beginnings as a tool for prototyping and manufacturing, it has now expanded to a wide range of industries, including healthcare, automotive, aerospace, fashion and food.
The technology has evolved to be smaller, more affordable and more user-friendly.
This has led to a proliferation of 3D printing in small businesses, schools, and even homes, making it accessible to a wider range of users.
Additionally, the materials that can be used for 3D printing have greatly expanded, allowing for more complex and detailed objects to be printed.
However, despite its growth and potential, 3D printing still faces challenges. Cost, lack of standardization and regulations, and environmental impact are some of the obstacles that need to be overcome.
But, as the technology continues to evolve, it's likely that these challenges will be addressed, and 3D printing will become even more mainstream.
Overall
3D printing is a technology that is worth keeping an eye on, as it has the potential to revolutionize many industries and change the way we live and work.
It's exciting to think about the possibilities of what can be achieved with this technology in the future, and how it will continue to change the world around us.
Let me know what you think in the comment section below






Comments